Table of contents
Fertility is a crucial aspect of human life, and many factors can affect it. While genetics and age play a significant role, lifestyle factors such as diet and nutrition can also impact fertility. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can promote reproductive health and increase the chances of conception. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of nutrients on fertility and the role of a healthy diet in promoting reproductive health.
Nutrients that can impact fertility
Macronutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, and fats provide the body with energy and help maintain hormonal balance. Adequate intake of these nutrients is essential for reproductive health.
Protein: Proteins are the building blocks of the body and play a vital role in the production of reproductive hormones. Foods rich in protein such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes can increase fertility in both men and women.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can improve fertility by regulating insulin levels and reducing the risk of ovulatory infertility.
Fats: Healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for reproductive health. Omega-3 fatty acids can improve sperm quality in men and regulate menstrual cycles in women. Foods rich in healthy fats include fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
Micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals also play a crucial role in fertility. These nutrients act as co-factors in enzymatic reactions that regulate reproductive hormones.
Vitamins: Vitamins such as vitamin D, vitamin E, and folate can improve fertility by regulating hormonal balance and improving egg quality. Foods rich in vitamin D include fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products. Vitamin E can be found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, while folate is abundant in leafy green vegetables, legumes, and fortified grains.
Minerals: Minerals such as zinc, selenium, and iron can also promote reproductive health. Zinc is essential to produce healthy sperm and can be found in oysters, lean meats, and legumes. Selenium can improve sperm motility and can be found in Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains. Iron is crucial for the production of red blood cells and can be found in lean meats, dark leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
The impact of a healthy diet on fertility
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet can improve fertility by regulating hormones and improving overall reproductive health. A diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can improve fertility in both men and women.
The role of diet in regulating hormones: Hormones play a crucial role in fertility, and diet can impact hormone balance. A healthy diet can regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation, and promote hormonal balance, leading to improved reproductive health.
The benefits of a healthy diet for both male and female fertility: A healthy diet can improve fertility in both men and women by improving sperm and egg quality, regulating menstrual cycles, and reducing the risk of ovulatory infertility.
Examples of nutrient-rich foods that can improve fertility: Foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are rich in essential nutrients that can improve fertility. Consuming a variety of these foods can help promote reproductive health.
Nutrients to avoid for optimal fertility
While some nutrients can improve fertility, others can have a negative impact. Certain types of fats, carbohydrates, and processed foods can reduce fertility and should be avoided.
Trans fats: Trans fats can increase insulin resistance and inflammation, leading to reduced fertility. Foods high in trans fats include fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks.
High-glycemic-index foods: Foods that are high in refined sugars and carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in insulin levels, leading to inflammation and hormonal imbalances that can negatively impact fertility. Examples of high-glycemic-index foods include white bread, white rice, and sugary drinks.
Processed foods: Processed foods are often high in sodium, preservatives, and additives, which can reduce fertility by increasing inflammation and disrupting hormonal balance.
Lifestyle factors that can impact fertility
In addition to diet, lifestyle factors such as exercise, sleep, and stress management can also impact fertility.
Exercise: Regular exercise can improve fertility by regulating hormones and reducing inflammation. However, excessive exercise can have the opposite effect and should be avoided.
Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is essential for reproductive health. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance, reduce sperm quality, and increase the risk of ovulatory infertility.
Stress management: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on fertility by disrupting hormone balance and reducing sperm and egg quality. Stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help promote reproductive health.
Conclusion
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet can promote reproductive health and increase the chances of conception. Adequate intake of essential nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals can improve fertility by regulating hormonal balance and improving overall reproductive health. Conversely, foods high in trans fats, refined sugars, and processed foods should be avoided. In addition to diet, lifestyle factors such as exercise, sleep, and stress management can also impact fertility. By making healthy choices and prioritizing reproductive health, individuals can increase their chances of conception and enjoy a healthy and fulfilling reproductive life.
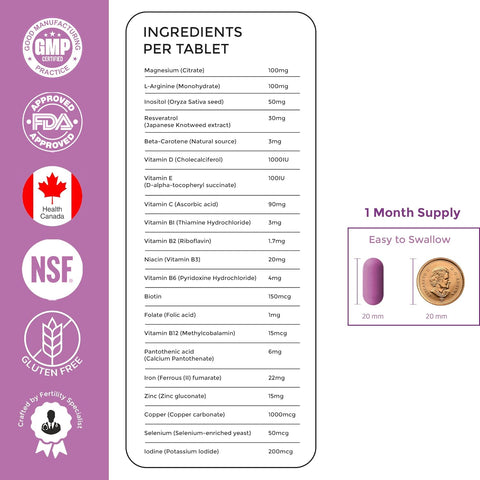
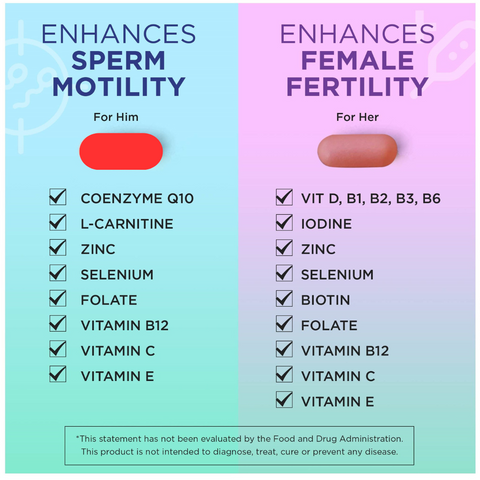
If you're looking to boost your fertility and prepare for a healthy pregnancy, consider adding natural prenatal supplements to your diet. Our supplements are specially formulated with essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, and antioxidants to support reproductive health and increase your chances of conception. By taking our supplements daily and following a healthy diet and lifestyle, you can give yourself the best chance of a successful and healthy pregnancy.
References:
- Chavarro, J. E., Toth, T. L., & Sadio, S. M. (2008). Diet and lifestyle in the prevention of ovulatory disorder infertility. Obstetrics and gynecology, 11(1), 39-47.
- Gaskins, A. J., & Chavarro, J. E. (2018). Diet and fertility: a review. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 218(4), 379-389.
- Hanson, M. A., & Gluckman, P. D. (2011). Developmental origins of health and disease: new insights. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology, 110(1), 5-6.
- Oostingh, E. C., Steegers-Theunissen, R. P., & de Vries, J. H. (2018). The effects of dietary patterns and micronutrients on female fertility. Reproductive biomedicine online, 36(6), 666-680.
- Ramlau-Hansen, C. H., Thulstrup, A. M., Nohr, E. A., Bonde, J. P., & Sørensen, T. I. (2007). Subfecundity in overweight and obese couples. Human reproduction, 22(6), 1634-1637.
- Vujkovic, M., de Vries, J. H., Lindemans, J., Macklon, N. S., van der Spek, P. J., Steegers, E. A., ... & Steegers-Theunissen, R. P. (2009). The preconception Mediterranean dietary pattern in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment increases the chance of pregnancy. Fertility and sterility, 94(6), 2096-2101.
























No comments yet.
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!
+ Open to leave a Comment